The ultimate guide to eDiscovery with Google Workspace and Google Vault

Modern collaboration tools have undoubtedly revolutionized the way we work. Messaging platforms like Slack have replaced in-person chat conversations, while video conferencing tools like Zoom have replaced traditional conference room meetings. Even the way we share documents has changed, with productivity suites like Google Workspace allowing for instant edits to shared files instead of exchanging hard copies.
As the use of these tools continues to expand, it’s crucial for legal teams to be well-equipped to handle the unique challenges they present. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Google eDiscovery, covering everything from retention and compliance to security and privacy.
Throughout this guide, we’ll explore:
- Basic features of Google Workspace
- Native features and limitations in Google Vault
- Your options for eDiscovery
- Bonus: An adaptive plan to help you get started with Google eDiscovery
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of your options for Google eDiscovery and be able to determine the best path forward for your team.
Let's dive in.
Google Workspace features
Google Workspace, previously known as G Suite and Gmail for Your Domain, is a comprehensive service package that offers productivity applications, collaboration tools, and cloud storage for both large and small businesses. The service includes 14 applications, namely:
- Gmail, the world’s most extensively used email service
- Drive, a private content repository that enables file and drive sharing
- Calendar, Google’s scheduling solution
- Meet, a group video and audio conferencing tool
- Chat, a secure communication and collaboration tool for teams
- Docs, a free web-based word processor
- Sheets, an online spreadsheet creation and editing tool
- Slides, a presentation program for creating, viewing, and editing presentations
- Sites, a structured wiki and web page creation tool
- Forms, a full-featured forms creation tool
- Keep, a note-taking service
- Jamboard, a digital whiteboard for real-time collaboration
- Apps Script, a cloud-based scripting language
- Cloud Search, a tool for finding content across Google Workspace
Millions of people worldwide rely on Google Workspace's leading communication apps, Gmail and Google Meet. The collaboration tools, Google Docs, Sheets, Slides, and Forms, enable teams to collaborate on documents, spreadsheets, and presentations in real-time. Google Workspace also includes advanced security and management tools such as Admin, Endpoint, Vault, and Work Insights for added productivity and data protection.
By subscribing to a Google Workspace plan, you get access to additional features that are not available with the free Google apps. With a subscription, you can set up a custom email account using your company's domain and enjoy business-level application features, 24/7 support via phone or email, extra storage, Microsoft Outlook integration, two-step authentication, and single sign-on (SSO) for added convenience.
Understanding your Google Workspace plan
To make sure your organization is prepared for eDiscovery, it's important to have a good understanding of your Google Workspace plan. Google offers various editions of Workspace, each with different capabilities tailored to meet the needs of different organizations.
For smaller organizations with up to 300 user accounts, the Google Workspace Business editions – Business Starter, Business Standard, and Business Plus – are the most suitable options. On the other hand, larger organizations with more than 300 accounts should consider the Enterprise Standard and Enterprise Plus editions.
You can find detailed information about the technical capabilities of each plan on Google Workspace's pricing page. However, when it comes to eDiscovery, it's essential to choose the edition that best fits your organization's size and requirements.
Google categorizes its Workspace editions based on the number of accounts, customer organization type, and capabilities. Here is a brief overview of the different editions available:
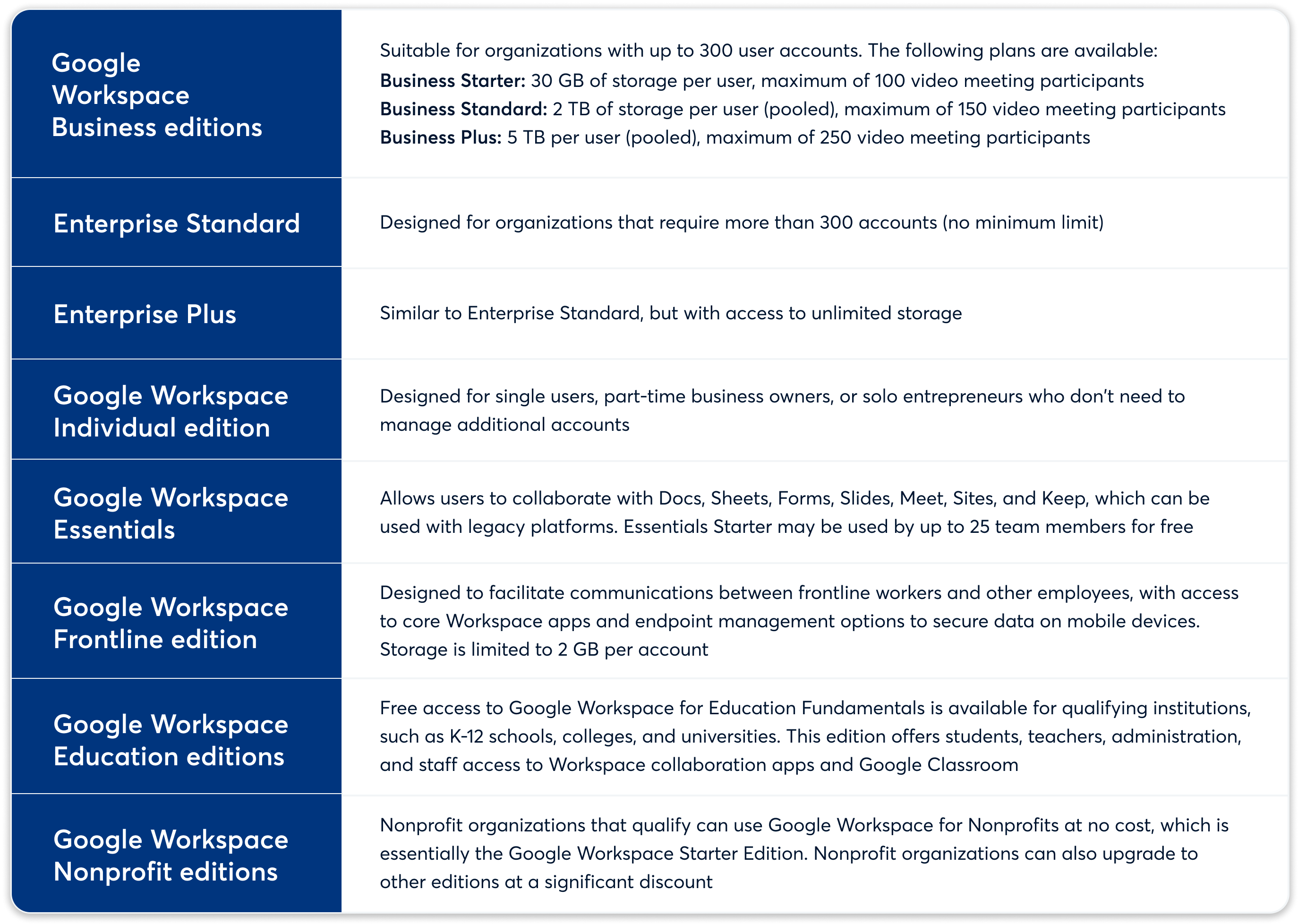
By understanding the different Google Workspace plans and their capabilities, you can ensure that your organization is well-prepared for eDiscovery.
What is Google Vault?
Google Vault is a cloud-based solution that provides organizations with tools to manage and retain their data in Google Workspace and other Google Cloud products. Vault is available as an add-on service for users with a Google Workspace Enterprise, Education, or Nonprofit edition. With Google Vault, you can:
- Search Google Workspace data for specific content
- Retain data for a set time or as long as necessary
- Delete data that is no longer needed by purging it from Google’s systems
Google Vault primarily assists organizations in complying with legal and regulatory requirements concerning data retention, with limited support for eDiscovery. Its key capabilities include:
- eDiscovery: Google Vault allows administrators to search each Google Workspace service individually, including Gmail, Google Drive, and Google Chat. Administrators can then choose to export the saved search results for legal and compliance purposes. Before exporting, administrators can preview the search results, and Vault keeps an audit trail of all the actions taken during the process.
- Legal holds: With Google Vault, organizations can place legal holds on specific data to ensure that it is not modified or deleted during the eDiscovery process. Administrators can set holds on individual accounts or groups of accounts and easily remove them when no longer needed.
- Retention policies: Google Vault enables organizations to establish retention policies for specific data types, preventing accidental deletion and ensuring compliance with data retention regulations. Retention policies can be customized and implemented for individual accounts or groups of accounts. This gives organizations control over their data, allowing them to preserve it through retention rules. These rules include default retention rules for all licensed users' data and custom retention rules with specific terms and conditions.

- Audit trails: Google Vault provides detailed audit trails that track user activity within the system. This can help organizations ensure that their data is being used appropriately and that any changes or deletions are properly documented.
Google Vault’s limitations
If you plan to manage and retain data in Google Workspace using Google Vault, it's essential to understand its limitations, which can affect your organization's ability to manage data effectively and conduct eDiscovery. Below, we've outlined some of the most significant Vault limitations that legal and IT teams typically encounter.
Limited data sources: Google Vault archives data solely from specific Google Workspace apps, such as Gmail, Google Drive, and Google Groups. If your organization uses other applications like Slack or Microsoft Teams, you'll need to use additional tools to archive and retain that data.
Limited data retention: Google Vault's retention policies have only a few options, such as retaining data indefinitely, for a set period, or until a specific event occurs. Although the retention period can be extended, it comes at an extra cost and isn't practical for long-term retention. If your organization needs long-term data retention, you may need to use additional tools or services.
Inability to modify data: Google Vault is designed to retain and archive data but cannot modify or delete it. This can be problematic if a legal or IT team needs to redact or delete certain data from the archive.
Limited collection capabilities: Google Vault only allows users to collect data from one source at a time. This limitation results in users having to duplicate their efforts to collect data from multiple sources.
Limited search capabilities: Google Vault's basic search interface may not be adequate for complex eDiscovery needs. The application's inability to perform unified searches across data sets, including those within Google, limits its usefulness. Although administrators can narrow down search results by using specific search criteria such as Boolean operators, wildcards, and proximity searches, it lacks advanced search capabilities like concept searching, fuzzy matching, or clustering. These search capabilities are commonly found in more advanced eDiscovery tools. As a result, it can be challenging to pinpoint relevant data using Google Vault alone
No real-time monitoring: Google Vault does not provide real-time monitoring of user activity, so it cannot alert an organization to potential issues or risks in real-time.
Limited reporting: While Google Vault provides basic reporting on search and retention activities, it lacks advanced reporting capabilities. This can be challenging for organizations that need to generate detailed reports for compliance or legal purposes.
Limited file types: Vault only supports a limited number of file types, such as Google Docs, Sheets, and Slides, which may pose a problem for organizations that use other file formats not supported by the tool.
Limited user management: Google Vault's user management is limited because all users must have admin rights. This limitation introduces access control challenges and risks.
Limited customization: Google Vault is a standard tool that cannot be customized to meet an organization's specific needs. While Vault is a good tool, it may not be the best fit for organizations that require more advanced eDiscovery or data retention capabilities.
Limited export options: Vault allows users to export data in only a few file formats, such as PST, MBOX, and JSON. This can be limiting if your organization needs to export data in a different format or preserve metadata associated with the data. Additionally, Vault's export capabilities are available only for a limited number of accounts and for one Google service at a time. Vault does not allow users to have multiple comparable exports or schedule programmed exports. The tool is not designed for large-scale or high-volume data backups and it is also limited in the types of metadata that it can export, such as metadata related to user activity or file permissions.
By understanding these limitations, your organization can make an informed decision about whether Google Vault is the right tool for your eDiscovery and data retention needs. If you require more advanced capabilities or need to work with data outside of the Google Workspace ecosystem, you may need to look into other solutions.
How to search and export Google Workspace data in Google Vault
To use Google Vault's eDiscovery capabilities, start by going to https://vault.google.com and signing in with your Google Workspace account. Once signed in, create a matter to manage your documents. Matters act as virtual bins that hold and display holds, searches, and exports you're working with, which you can review within the Workspace platform. A matter typically includes lists of saved search queries, holds, accounts shared with the matter, and exports.
After creating your matter, you can share it with other users to collaborate and leverage different options to search and retrieve pertinent ESI evidence. Within matters, you can create legal holds to pull relevant data by document type, date range, user account, and department. You can also narrow and refine your searches with Boolean shortcuts, and filter by criteria to save time collecting relevant data.
Once you've created your matter, a Search tab will open up. This is where you can begin your search by entering your search parameters and choosing which accounts to search and other conditions. To get started, follow these steps:
- Find messages sent by specific users by entering an email address in the Account email addresses field or by using search operators.
- Find messages with a specific phrase by grouping words into phrases with quotation marks.
- Exclude drafts to remove draft messages from your search results.
- Exclude matches by putting a hyphen before the search term.
- Click Count to report the number of results faster than a full search if you're concerned that your search will return too many results and extend processing time.
- Click Expand to refine your search and edit your search parameters.
- Click Search. After the search completes, Vault opens a table of the results.
- Preview your results. To preview a matching item in the table of results, click a row and the preview opens in a sidebar on the right.
- Click Save to save your query. After you finalize your search parameters, you can save the query to quickly run this search again later.
- Click query to open a saved query. When you run the search again, the results include data created since the last time you searched.
To export and analyze your results, go to the Exports tab and track the progress of your export. Once it's complete, click Download to retrieve your exported files. Note that you have 15 days after the export starts to download the files.
Exporting in Google is not synonymous with downloading. To download your exported files, you will need to go to the Exports section within the matter and download the files from there. You will then need to re-upload the data to your review platform.

It's important to note that although Google Vault can be useful for preservation and collection, it cannot be used alone for search, review, and production. You'll still need to import Google's data (and discoverable data from any other sources) into your eDiscovery solution to process and review all your data in one place.
What about Google Takeout?
Google Takeout is a free tool that lets users export all their Google data into a single downloadable file, which includes 51 different types of data such as email, calendars, bookmarks, and even YouTube activity. It also allows users to export their photos and free up space on their Drive by archiving old and unused files.
However, it’s not recommended to use Google Takeout as a backup solution for an organization. Although data can be downloaded and exported, the tool does not provide security and restoration abilities in case of unexpected deletions or attacks that could result in data loss. There are some risks to consider if an organization is thinking about using Google Takeout as a backup solution:
- Restoration issues. Google Takeout allows users to schedule automatic downloads of their data every two months, but this infrequency could cause restoration issues if they need to recover data that was lost more recently.
- Security risks. Once data has been downloaded, it's vulnerable to copying and sharing without a user’s knowledge, compromising its confidentiality.
- Compatibility concerns. Files downloaded with Google Takeout may not be compatible with other tools, which could create issues when trying to open or work with them in different programs or platforms. For example, documents created with Google Sheets may not be opened with Microsoft Word or Excel.
- Lack of control. Unlike backup solutions that allow administrators to easily restore data when necessary, Google Takeout requires administrators to log in on behalf of the user to access and download data. Alternatively, an administrator can block Google Takeout entirely, preventing users from exporting and downloading any data.
Google Takeout might be a good solution for simple exporting needs that don't require all the preservation options included in Google Vault. However, note that Google Takeout does not prevent users from deleting data from their accounts, which makes it critical to know precisely the data you need in advance. Additionally, you cannot filter by date or any other criteria except by Google product, so any data on your account for that particular application will be exported.
Optimize your efforts with a Google eDiscovery plan
If you're just starting out with Google eDiscovery or have already begun some kind of initiative, we believe these steps are crucial to employing a successful Google eDiscovery plan.
Step 1: Understand your needs
The first step in creating an effective Google eDiscovery plan is to assess your needs. To do this, ask yourself questions such as:

Regardless of the size of your organization, if your Google account holds critical information, it should be easily accessible, useful, and secure. If it's not meeting those standards, it's time to reevaluate your Google eDiscovery efforts.
Step 2: Reassess your Google Workspace plan
Once you have a better understanding of your needs, ensure that your current Google Workspace subscription supports them. If it doesn't, upgrading to one of Google’s Workspace Business plans is highly recommended to achieve ultimate visibility and access to your data. If you don't already have a Business Standard, Business Plus, Enterprise Standard, or Enterprise Plus plan, obtaining one is essential. Without it, you won't have the visibility and control necessary to develop a successful Google eDiscovery strategy.
Step 3: Establish a company Google policy
Once you have aligned your needs with your Workspace plan, it's important to put everything in writing. A good starting point is to create a company-wide "Google policy" that outlines the people, processes, and technology necessary for successful use, governance, and discovery of Google Workspace data. Although Google policies may differ depending on company size, needs, and maturity, there are some basics to consider:
- Outlining which user roles should be assigned to whom and configuring permissions accordingly
- Optimizing admin roles and user permissions for compliance and security
- Identifying relevant data types to retain or delete and explaining the reasoning behind it
- Implementing controls and restrictions around user behavior and clarifying why they are necessary
- Identifying current limitations and detailing plans to address those gaps in the future
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, a well-documented policy can streamline communication between teams, help identify and mitigate risks, and enable continuous iteration and improvement of your Google eDiscovery processes.
Step 4: Implement an eDiscovery solution
Most enterprises may find Google's enterprise-level controls for preservation and search features useful. However, relying solely on Google Vault is insufficient to support long-term strategy and business objectives. This is because organizations use various communication, collaboration, and content apps, and as more applications are adopted, the eDiscovery challenge becomes more significant, and more data needs to be controlled. Therefore, implementing a trusted eDiscovery tool can help you forensically process and search all your application data, making your Google eDiscovery plan more robust.
Many companies believe that they overspend on an in-house solution because litigation occurs infrequently. However, the opposite is true. Waiting for litigation to strike wastes millions of dollars, and a proactive approach is more cost-effective.
When selecting a Google eDiscovery solution, ensure it has the following features:

Apart from these Google-specific features, your eDiscovery software should also have flexible deployment options, top-tier security measures, and compatibility with review platforms. By bringing a Google eDiscovery solution onboard, you can streamline your eDiscovery process and save yourself a lot of money and headaches in the long run.
Step 5: Make a long-term eDiscovery and preservation plan
As technology continues to evolve, the complexity of information governance increases. To effectively manage this complexity, it is crucial to have a sustainable, enterprise-grade eDiscovery solution that can adapt to new technology. While litigation is not a desired outcome, it is important to consider the bigger picture when choosing a Google eDiscovery solution.
While it may be tempting to prioritize cost and ease-of-use for Google specifically, it is important to consider the needs of all enterprise applications that your organization uses. In addition to Google Workspace, you may also be using Slack, Microsoft Teams, Jira, and many other applications that generate potentially responsive data. As such, it is important to choose a comprehensive eDiscovery solution that can serve as a "master tool" for your entire tech stack. By doing so, you can ensure long-term value for your organization and streamline the eDiscovery process across all applications.
And there you have it. We hope our guide has provided you with a deeper understanding of Google Workspace and Google Vault, their discovery capabilities and limitations, as well as how to create an effective Google eDiscovery plan for your business. It's important to remember that implementing your plan is only the first step. It's an ongoing process that requires constant education and guidance for your workforce, especially as new technologies emerge. With consistent effort and refinement, you can stay ahead of potential challenges and ensure a smoother eDiscovery process in the long run.
Why you need Onna for Google Workspace
Onna offers a new approach to managing Google Workspace and other application data by streamlining the discovery process, supercharging early case assessment, and providing a single workflow across all applications.
Onna’s Data Management Platform seamlessly integrates with Google Workspace to collect and process all data in real-time, ensuring consistent collection, processing, and search of data from leading content, collaboration, and chat apps. By eliminating cumbersome steps from your eDiscovery process, such as exporting data from Gmail and Google Drive via separate workflows or uploading multiple files individually for early case assessment, Onna makes it easy to bring all your data together and cull it down to only the most relevant information. This results in a more targeted and accurate dataset that you can send for review.
Onna makes it easy to:
- Reduce the risk of lost or corrupt data by using a single workflow
- Benefit from enhanced metadata capture through a single loadfile
- Drive early case assessment searches across Vault data to reduce review costs
If you're seeking a data management platform that shares the same philosophy as Google's apps – cloud-based, available from anywhere, and user-friendly – then Onna is the perfect choice. By simplifying the eDiscovery process, Onna empowers companies to manage their data effectively and efficiently.
Sound like the solution you’re looking for? Read more about our Google Workspace connector here.
Other posts you might be interested in
View all posts
eDiscovery
5 min read
What you need to know about eDiscovery with Google Workspace
Read more
eDiscovery
7 min read
Cutting review costs: How to overcome collection challenges for Google Workspace data
Read more
News & Updates
2 min read
 eDiscovery
eDiscovery Collections
Collections Processing
Processing Early Case Assessment
Early Case Assessment Information Governance
Information Governance Data Migration
Data Migration Data Archiving
Data Archiving Platform Services
Platform Services Connectors
Connectors Platform API
Platform API Pricing Plans
Pricing Plans Professional Services
Professional Services Technical Support
Technical Support Partnerships
Partnerships About us
About us Careers
Careers Newsroom
Newsroom Reveal
Reveal Logikcull by Reveal
Logikcull by Reveal Events
Events Webinars
Webinars OnnAcademy
OnnAcademy Blog
Blog Content Library
Content Library Trust Center
Trust Center Developer Hub
Developer Hub